Everything You Need to Know About CBN

CBN, short for cannabinol, is one of the 110+ cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant. Due to its typically low concentrations in hemp, it’s considered a “minor cannabinoid.” However, it has been gaining increased attention recently due to its role in promoting health and wellness. In fact, scientific research on cannabis has concentrated on what are referred to as the “big six” cannabinoids due to the significance of their impact on the human body. CBN is one of the big six.
But in order to understand why CBN is so special, we must first understand how the family of phytocannabinoids is connected.
The family of phytocannabinoids
The family of cannabinoids is closely intertwined. Cannabinoid production starts when geranyl pyrophosphate and olivetolic acid combine and form CBGA, triggered by an enzyme. CBGA then can become THCA, CBDA or CBCA through the work of separate synthase enzymes. At this point, the process of decarboxylation kicks in and converts these cannabinoids from their acidic forms to their “heated” forms - THC, CBD, and CBC. The heating process essentially activates these cannabinoids and allows them to bind directly to cannabinoid receptors in the body.
So, what about CBN? CBN is typically the oxidation product of THC, although it can be derived from other cannabinoids. Because CBN is created from exposure to light and oxygen, it’s typically formed during the drying phase of cannabis processing and is often most abundant in older harvests.
Remember CB1 and CB2 receptors? If not, here’s a quick refresher: CB1 receptors are located within your central nervous system, brain, and spinal cord. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are located in the peripheral nervous system, brain, immune system, and gut.
While CBN is an agonist of both CB1 and CB2 receptors, it has a low affinity for CB1 and binds preferentially to CB2.
For a quick-reference guide to the difference between CBN and CBD, check out the infographic below.
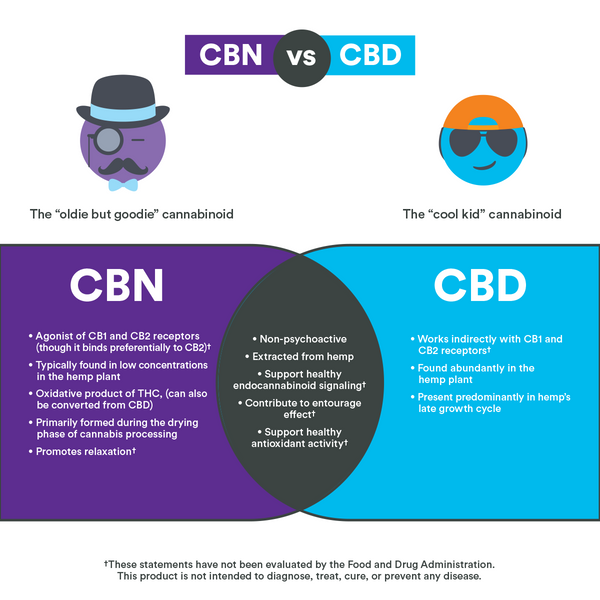
What are the benefits of CBN?
In full-spectrum blends, CBN works harmoniously with CBD and the other cannabinoids to promote the “entourage effect” - that old plant magic where the whole is greater than the sum of its parts, and all the compounds in cannabis work together to maximize health and wellness impact.
Additionally, CBN has been found to support relaxation and unwinding at the end of the day. Plus, when combined with terpenes, blends like Downshift have even more benefits. Downshift features linalool, which is derived from Camphor tree, and beta-caryophyllene, which is derived from clove. These terpenes provide a warm, earthy, herbaceous aroma and taste to this formulation. However, they do much more than just smell good - these terpenes have also been shown to support healthy antioxidant activity and healthy inflammatory markers.†









